In the ever-evolving landscape of medical diagnostics, Computed Tomography (CT) scans have emerged as a powerful and versatile tool, revolutionizing the way healthcare professionals visualise and diagnose a wide array of medical conditions. This non-invasive imaging technique provides detailed cross-sectional images of the body, offering invaluable insights into the structure and function of organs, tissues, and bones. In this article, we explore the significance of CT scans as a diagnostic tool and their role in enhancing patient care.
Understanding CT Scan Technology:
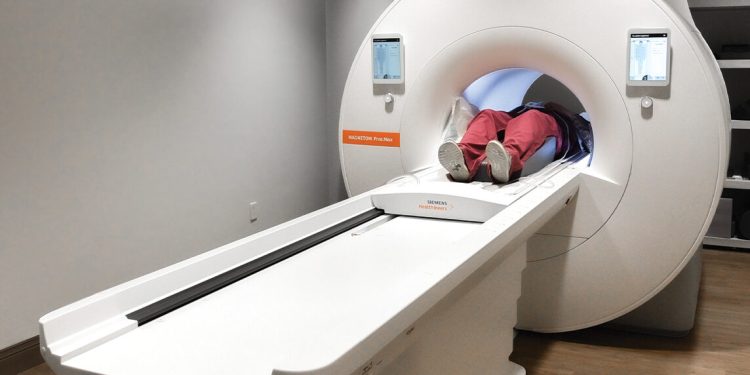
A CT scan, also known as a CAT (Computed Axial Tomography) scan, utilises X-rays and advanced computer technology to generate detailed cross-sectional images, or slices, of the body. Unlike traditional X-rays, which produce two-dimensional images, CT scans offer three-dimensional reconstructions, allowing healthcare professionals to examine internal structures with unparalleled precision.
The Procedure:
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a motorised table that moves through a doughnut-shaped machine called a gantry. The gantry houses an X-ray tube that rotates around the patient, emitting X-ray beams from multiple angles. Detectors on the opposite side of the gantry capture the X-rays after they pass through the body, and a computer processes the data to create detailed images. Contrast agents may be used to enhance visibility of certain structures or abnormalities.
Versatility in Diagnostics:
CT scans are highly versatile and can be employed to investigate a myriad of medical conditions across various specialties:
- Trauma and Emergency Medicine:
- Rapid assessment of injuries, including fractures, internal bleeding, and organ damage.
- Swift decision-making in emergency situations, guiding timely interventions.
- Oncology:
- Detection and staging of tumors.
- Monitoring the response to cancer treatments.
- Guiding surgical planning and radiation therapy.
- Neurology:
- Visualizing the brain and spinal cord for conditions such as strokes, tumors, and hemorrhages.
- Assessing structural abnormalities and guiding neurosurgical procedures.
- Cardiology:
- Evaluation of coronary arteries for blockages.
- Assessment of cardiac anatomy and function.
- Detection of vascular diseases and aneurysms.
- Gastroenterology:
- Diagnosis of gastrointestinal conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease and cancers.
- Evaluation of liver, pancreas, and gallbladder abnormalities.
- Orthopedics:
- Visualization of bones and joints for fractures, arthritis, and degenerative conditions.
- Pre-surgical planning for orthopedic procedures.
Advantages of CT Scans:
- Speed and Efficiency:
- CT scans provide quick results, making them particularly valuable in emergency situations.
- Rapid imaging helps reduce patient discomfort and anxiety.
- High Resolution:
- The ability to capture detailed images allows for the identification of subtle abnormalities.
- Precise visualization aids in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Non-Invasiveness:
- CT scans eliminate the need for invasive procedures in many cases, reducing patient risk and discomfort.
- Post-surgical follow-up can be conducted without additional invasive measures.
- Wide Applicability:
- CT scans can be applied to virtually any part of the body, making them a versatile diagnostic tool across medical specialties.
Challenges and Considerations:
While CT scans offer numerous benefits, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks, such as exposure to ionizing radiation. Healthcare providers carefully weigh the risks and benefits, particularly in cases where repeated imaging may be necessary. Innovations in technology, such as low-dose CT scans, aim to mitigate radiation exposure while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
The advent of CT scans has significantly advanced the field of diagnostic medicine, providing healthcare professionals with a powerful tool to investigate and understand a broad spectrum of medical conditions. From emergency situations to routine screenings, CT scans play a crucial role in enhancing patient care, enabling early detection, accurate diagnosis, and informed treatment decisions. As technology continues to evolve, the future promises even more refined and patient-friendly imaging techniques, further solidifying the pivotal role of CT scans in modern healthcare.